Aspergillus nidulans holds significant importance in the fields of genetics and cell biology. Here are a few key reasons:
- Model Organism: A. nidulans is widely recognized as a model organism for studying various cellular processes. Its genetic makeup and ease of manipulation make it ideal for genetic studies. Researchers use it to investigate fundamental biological processes such as gene regulation, cell division, and metabolism.
- Genetic Mapping: A. nidulans has a well-characterized genome, which aids in the mapping and identification of genes. By studying the effects of mutations and observing phenotypic changes, scientists can gain insight into the function of specific genes and their role in cellular processes.
- Sexual Reproduction: Unlike many other fungi, A. nidulans exhibits sexual reproduction, allowing researchers to explore the genetics of mating and meiosis. This capability makes it a valuable tool for studying genetic recombination, genetic inheritance, and the evolution of sexual reproduction.
- Secondary Metabolites: A. nidulans has a propensity to produce secondary metabolites, including antibiotics and other bioactive compounds. Researchers use these metabolites for drug discovery and understanding the genetic regulation of secondary metabolism.
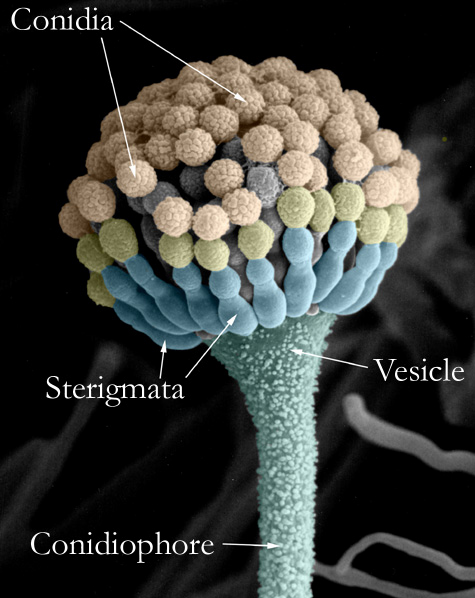
- Cellular Differentiation: A. nidulans can undergo various differentiations, forming complex multicellular structures called conidiophores. This process makes it an excellent model for studying cellular differentiation, signaling pathways, and morphogenesis.
In summary, A. nidulans serves as a versatile and valuable organism for understanding genetics and cell biology. Its easy manipulation, well-characterized genome, and diverse biological features make it an excellent choice for scientific investigations in these fields.